Pourfour du Petit syndrome caused by traumatic pseudo-aneurysm of the internal carotid artery
* Rodrigo Becco de Souza (a), Guilherme Brasileiro de Aguiar (a), Jefferson Walter Daniela (a), Mário Luiz Marques Contia (a) and José Carlos Esteves Veiga (b)
(a) Department of Surgery, Division of Neurosurgery, Santa Casa Medical School, São Paulo, Brazil
(b) Department of Neurosurgery, Santa Casa Medical School, São Paulo, Brazil
Received 10 December 2012
Revised 8 January 2013
Accepted 14 January 2013
Abstract. Pourfour du Petit syndrome, or reverse Horner syndrome, is described as an overactive sympathetic nervous system, being characterized by mydriasis, eyelid retraction, and hyperhidrosis. We described a case of Pourfour du Petit syndrome after cervical injury by gunshot, with a little review about this rare syndrome. Angiography revealed dissection and formation of pseudo aneurysm of the left carotid artery. We believe that this lesion caused hyper-stimulation of the left cervical sympathetic chain, resulting in reverse Horner syndrome or Pourfour du Petit syndrome. There was reversal of symptoms spontaneously after 3 wk.
Keywords: Horner syndrome, autonomic nervous system, Pourfour du Petit syndrome, carotid artery dissection
1. Introduction
Horner syndrome is, characterized by ptosis, miosis, and hemifacial anhidrosis, caused by inhibitory, lesion in the ipsilateral cervical sympathetic chain [1]. Pourfour du Petit (PDP) syndrome, or reverse Horner syndrome is, described as an overactive sympathetic nervous system being, characterized by mydriasis, eyelid retraction, and hyperhidrosis [2].
The present case report describes a case of a patient; victim of gunshot wound in the cervical region that showed the reverse Horner syndrome. We also carry out a brief review of the literature on the subject.
2. Case report
A male patient, 16 yr, was victim of a gunshot wound in the cervical region; bullet entry was in the left submandibular region, transfixing the cervical spine. The patient was found unconscious by the rescue team with signs of respiratory failure, and underwent endotracheal intubation. He underwent a head computed tomography, which showed ischemic area in the left cerebral hemisphere. The patient underwent intensive care under sedation, until clinical and hemodynamic stabilization. Diagnostic complementary assessment with brain angiography demonstrated evidence of dissection of the left internal carotid artery in its cervical segment with pseudo aneurysm formation (Fig. 2).

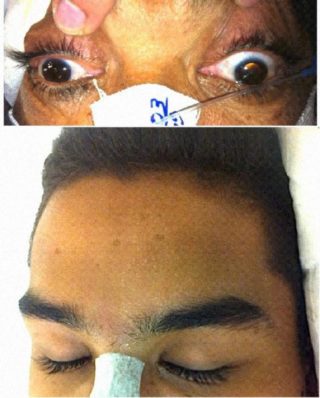
After discontinuation of sedation, a neurological examination revealed anisocoria (left larger than right), as showed in Fig. 1. When in a dark room, unlike Horner syndrome, the difference between pupil sizes decreased. When one eye was illuminated (left or right), both pupils contracted. The left side of the face showed sweating (Fig. 1) and mild blush. The mydriasis associated with hyperhidrosis and ipsilateral eyelid retraction characterized PDP syndrome.
The patient was still aphasic due to ischemia in the left carotid territory, he was underwent endovascular treatment of carotid dissection. Patient evolution showed reversal of the syndrome, and he was iso choric 3 weeks after the event with improvement of general status.
Dr. Rodrigo Becco
Médico neurocirurgião graduado pela Universidade de São Paulo (USP), em 2007. Residente em Neurocirurgia pela Santa Casa de São Paulo, em 2014. Mestre pelo Instituto de Assistência Médica do Servidor Público Estadual, em 2015. Membro da Sociedade Brasileira de Neurocirurgia desde 2014.

